How to Use Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
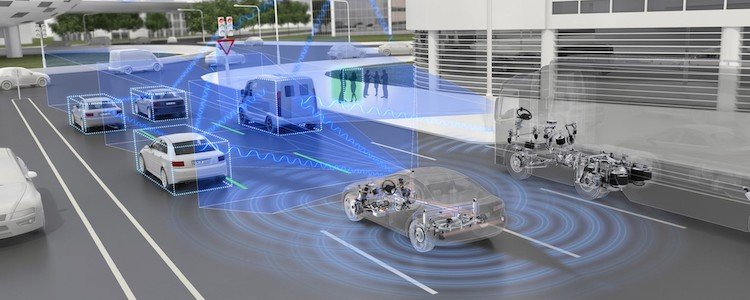
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are revolutionizing the driving experience by enhancing safety, convenience, and efficiency on the road. These systems use a combination of sensors, cameras, and software to assist drivers in navigating various driving conditions. Understanding how to use Advanced Driver Assistance Systems effectively can greatly improve your driving experience and help prevent accidents. In this article, we’ll explore the different features of ADAS and provide tips on how to use them.

Understanding the Basics of ADAS
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems are designed to provide support to drivers in a variety of ways. By leveraging technology, these systems can monitor the surroundings of the vehicle, warn of potential hazards, and even take control in certain situations to prevent accidents.
Common Features of ADAS
Some of the most common ADAS features include:
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): This feature adjusts your vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the car in front of you. It’s particularly useful in highway driving and traffic conditions.
- Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): This system helps prevent unintentional lane departure by gently steering the car back into its lane if it begins to drift.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): AEB systems detect potential collisions and automatically apply the brakes to prevent or reduce the severity of an accident.
- Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): This feature alerts drivers when a vehicle is in their blind spot, helping to prevent accidents during lane changes.
How to Use Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive Cruise Control is one of the most popular features of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems. To use it effectively, follow these steps:
- Activate the System: Turn on ACC by pressing the cruise control button on your steering wheel. This may require setting a specific speed.
- Set Your Desired Speed: Use the control buttons to adjust the speed to your preference. ACC will maintain this speed unless it detects a slower vehicle ahead.
- Adjust Following Distance: Most ACC systems allow you to set the distance you want to maintain from the car in front. This can usually be adjusted using buttons on the steering wheel.
- Monitor the System: Always keep your hands on the wheel and eyes on the road. ACC is a supportive tool, not a replacement for attentive driving.
Using Lane Keeping Assist Safely
Lane Keeping Assist is another essential component of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, designed to prevent lane drift and keep the vehicle centered. Here’s how to use it:
- Enable Lane Keeping Assist: Activate LKA through a button on your dashboard or steering wheel.
- Understand Visual and Audio Warnings: Familiarize yourself with the warning signals that the system uses, such as beeps or dashboard lights, to alert you when you’re about to leave your lane.
- Trust but Verify: While LKA can gently steer your vehicle back into the lane, you should always be prepared to take over. Never rely solely on the system to drive for you.
Maximizing the Benefits of Automatic Emergency Braking
Automatic Emergency Braking is a life-saving feature that can prevent rear-end collisions. To make the most of this feature:
- Ensure the System is On: AEB is usually active by default, but it’s a good idea to check your vehicle settings to ensure it is enabled.
- Stay Alert: Although AEB can react faster than a human in many situations, it’s crucial to remain vigilant and ready to brake manually if necessary.
- Regularly Maintain Sensors: Keep your vehicle’s sensors clean and free from obstructions, as dirt or debris can impair the system’s functionality.
Making Use of Blind Spot Monitoring
Blind Spot Monitoring is an excellent feature for enhancing safety during lane changes. Here’s how to use it effectively:
- Activate the System: BSM is typically active when the vehicle is started, but double-check the settings if you’re unsure.
- Observe the Indicators: Most vehicles have indicators on the side mirrors that light up when there is a vehicle in your blind spot. Some systems also provide audible alerts.
- Use in Conjunction with Mirrors: While BSM is helpful, it should not replace checking your mirrors and over your shoulder before changing lanes.
Conclusion
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems have greatly enhanced vehicle safety and convenience, but they are most effective when used correctly. By understanding and properly utilizing features like Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Keeping Assist, Automatic Emergency Braking, and Blind Spot Monitoring, you can enjoy a safer, more comfortable driving experience. Always remember that these systems are designed to assist, not replace, the driver. Staying alert and practicing safe driving habits will ensure you get the most out of your vehicle’s ADAS technology.