How Autonomous Vehicles Work
With advancements in technology, the future of transportation is here. One of the most exciting developments is autonomous vehicles, commonly known as self-driving cars. But how do autonomous vehicles work? These cutting-edge machines combine various technologies to navigate, make decisions, and transport passengers without human intervention. Understanding how autonomous vehicles work can help you appreciate the technology that powers them and the potential they have to revolutionize our daily lives.
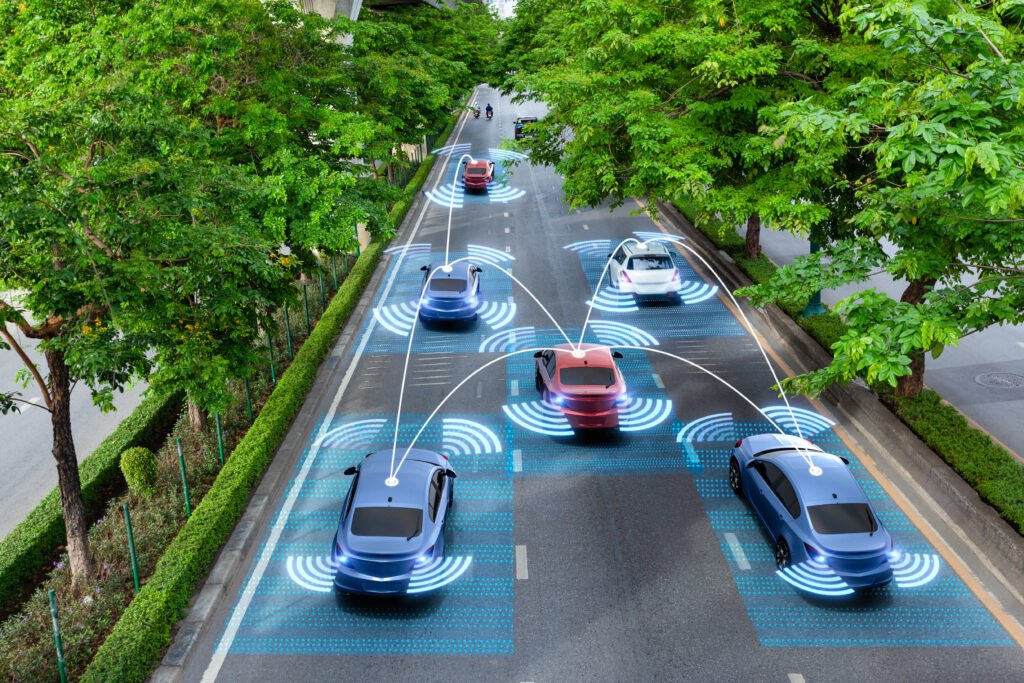
The Technology Behind Autonomous Vehicles
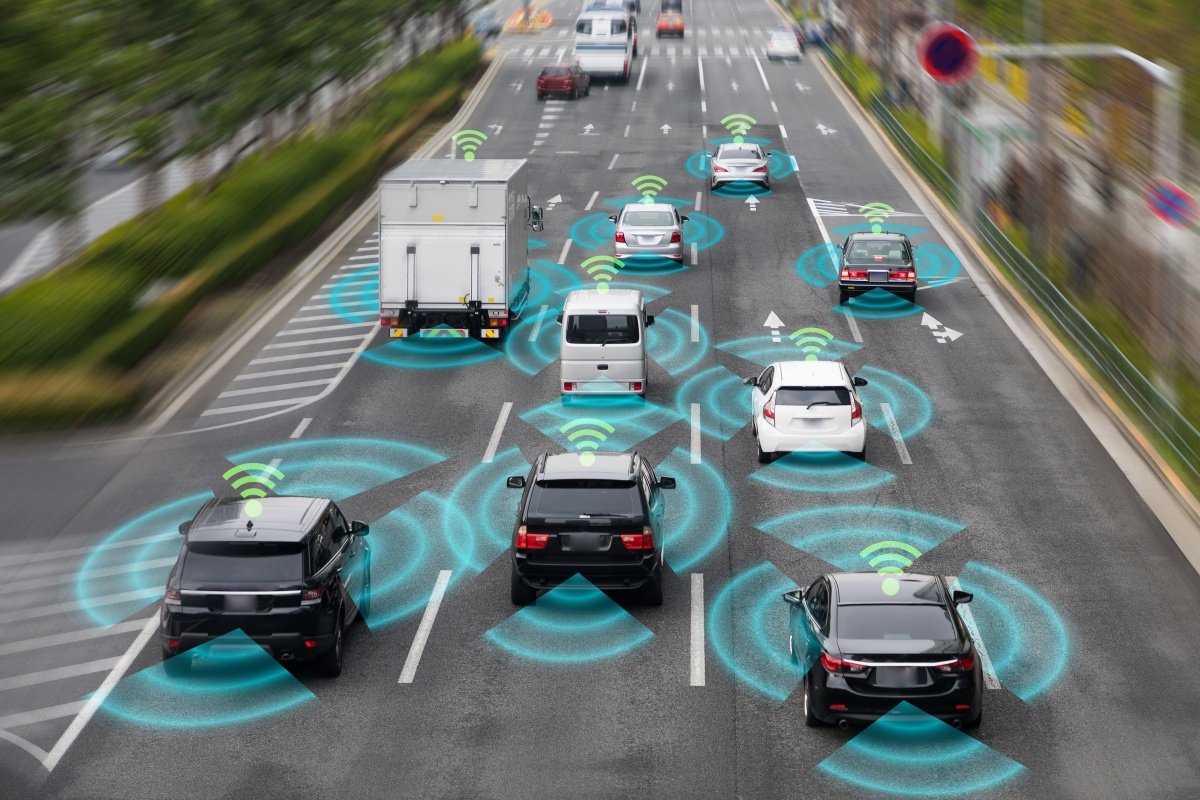
Autonomous vehicles rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI) to perceive their surroundings and make decisions. These systems work together to create a detailed map of the environment around the vehicle.
- Sensors and Cameras: Sensors and cameras play a crucial role in how autonomous vehicles work. Cameras placed around the vehicle capture visual information, such as lane markings, traffic signals, and obstacles. Meanwhile, sensors like Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) emit laser pulses to measure distances and detect objects around the car. These sensors provide a 360-degree view, helping the vehicle understand its immediate environment.
- Radar Systems: Radar technology is another key component in autonomous vehicles. Radar sensors use radio waves to detect the speed and distance of objects, such as other vehicles and pedestrians. This information is essential for maintaining safe distances and avoiding collisions. Radar is particularly useful in adverse weather conditions, such as rain or fog, where cameras and Lidar may be less effective.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are at the heart of how autonomous vehicles work. AI systems process the data collected by sensors and cameras to identify patterns, recognize objects, and predict the actions of other road users. Machine learning algorithms allow the vehicle to learn from past experiences, improving its decision-making abilities over time.
The Role of Mapping and GPS in Autonomous Vehicles
Mapping and GPS technology are vital for autonomous vehicles to navigate accurately. High-definition maps provide detailed information about the roads, including lane configurations, speed limits, and traffic signals. These maps are continually updated to reflect real-time changes, such as road construction or traffic incidents.
- GPS Navigation: GPS (Global Positioning System) helps autonomous vehicles determine their precise location on the road. By combining GPS data with high-definition maps, the vehicle can plan its route and follow it accurately. GPS also assists in locating the vehicle within a few centimeters, which is crucial for tasks like lane-keeping and making turns.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Autonomous vehicles constantly process real-time data from their surroundings. This includes information from sensors, cameras, and radar, as well as GPS and map data. By integrating all these data sources, the vehicle can make informed decisions about speed, direction, and braking to ensure safe and efficient travel.
How Autonomous Vehicles Make Decisions
One of the most fascinating aspects of how autonomous vehicles work is their decision-making process. These vehicles use a combination of pre-programmed rules, real-time data analysis, and machine learning to make split-second decisions.
- Path Planning: Path planning involves determining the best route for the vehicle to take, considering factors like traffic conditions, road layout, and obstacles. Autonomous vehicles continuously evaluate multiple routes to find the safest and most efficient path to their destination.
- Object Detection and Classification: Autonomous vehicles must identify and classify objects in their surroundings, such as pedestrians, cyclists, other vehicles, and road signs. By recognizing these objects, the vehicle can predict their behavior and respond accordingly. For example, if a pedestrian is crossing the street, the vehicle will slow down or stop to avoid a collision.
- Control Systems: Control systems manage the vehicle’s steering, acceleration, and braking. Once the AI makes a decision, the control system executes the necessary actions to carry it out. For instance, if the vehicle needs to change lanes, the control system adjusts the steering to make the maneuver smoothly and safely.
Challenges and Future of Autonomous Vehicles
While the technology behind autonomous vehicles is impressive, there are still challenges to overcome. Issues such as handling complex urban environments, ensuring cybersecurity, and gaining public trust are significant hurdles. However, ongoing research and development are continually improving how autonomous vehicles work.
The future of autonomous vehicles is promising. With advancements in AI, sensor technology, and mapping, these vehicles will become safer, more reliable, and widely available. Understanding how autonomous vehicles work can help us appreciate their potential to transform our transportation systems, reduce accidents, and improve traffic flow.

